Stopwatch and timer calibrations are perhaps the most common calibrations performed in the field of time and frequency metrology. Hundreds of laboratories and metrology institutes calibrate many thousands of timing devices annually to meet legal and organizational metrology requirements.
There are three generally accepted methods for calibrating a stopwatch or timer: the direct comparison method, the totalize method, and the time base method. The first two methods consist of time interval measurements that compare the time interval display of the DUT to a traceable time interval reference. In the case of the direct comparison method, the time interval reference is normally a signal broadcast, usually in the form of audio tones. In the case of the totalize method, the time interval reference is generated in the laboratory using a synthesized signal generator, a universal counter, and a traceable frequency standard. The third method, the time-based method, is a frequency measurement. It compares the frequency of the DUT's time-base oscillator to a traceable frequency standard.
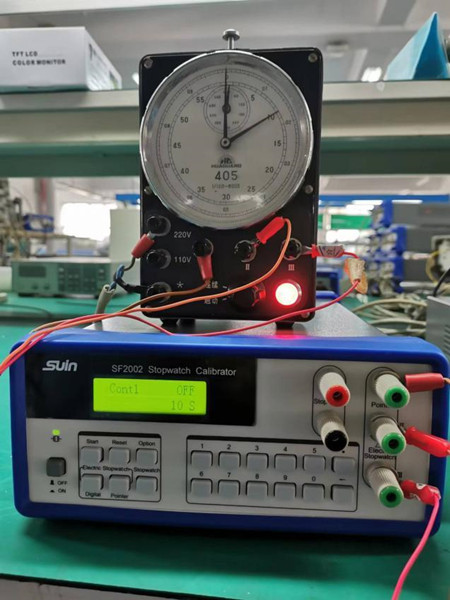
Suin SF2002 stopwatch calibrator is an easy-operating and high-precision instrument that adapts the totalize method, which can calibrate electric stopwatches (405,407,408,415/417), mechanical stopwatches and digital quartz electronic stopwatches.
It can not only calibrate one stopwatch but also several ones with several fixtures, which meet different requirements, just like below pictures shown.

If you want to know more information about it, please contact us for its User's manual or operation video.